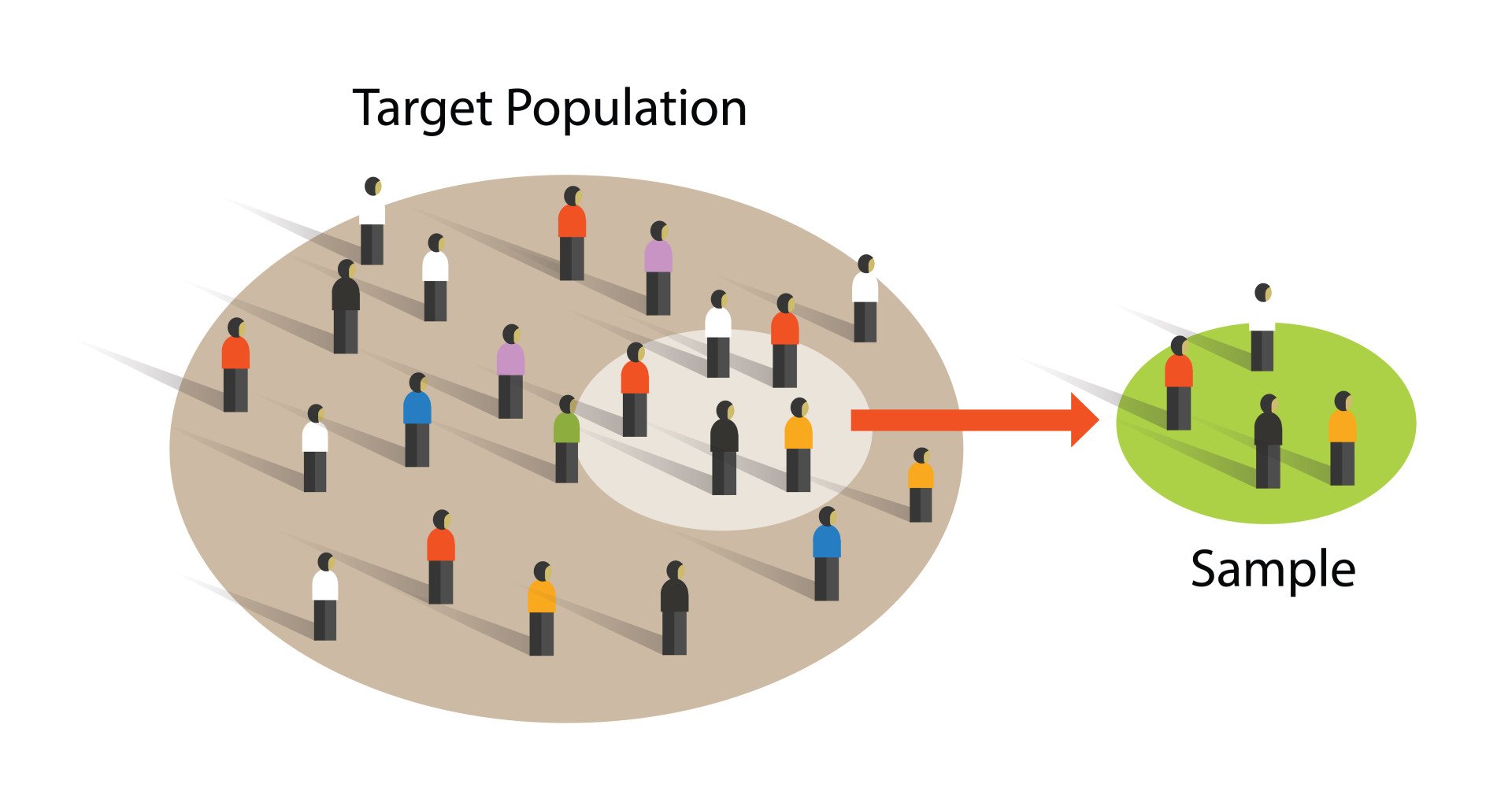
What Is Simple Random Sampling?
Simple random sampling is a technique in which each member of a population has an equal chance of being chosen through an unbiased selection method. Each subject in the sample is given a number, and then the sample is chosen randomly.| Simply Psychology