Version 14.1 gains computational advances for human and AI users. Detailed examples of new and expanded features: semantic search, LLMs, symbolic arrays, binomial coefficients, differential and difference equations, PDEs, biomolecules, neural nets, dates, videos, speech recognition, geography, astronomy, geometry, notebooks, natural language input, diffs, compiler, external languages.| writings.stephenwolfram.com
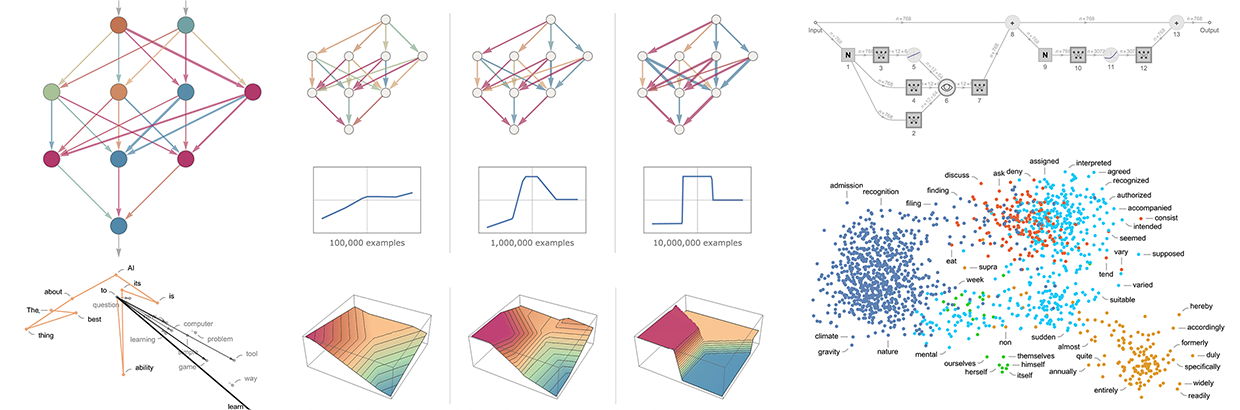
Stephen Wolfram explores the broader picture of what's going on inside ChatGPT and why it produces meaningful text. Discusses models, training neural nets, embeddings, tokens, transformers, language syntax.| writings.stephenwolfram.com