Sampling Methods In Research: Types, Techniques, & Examples
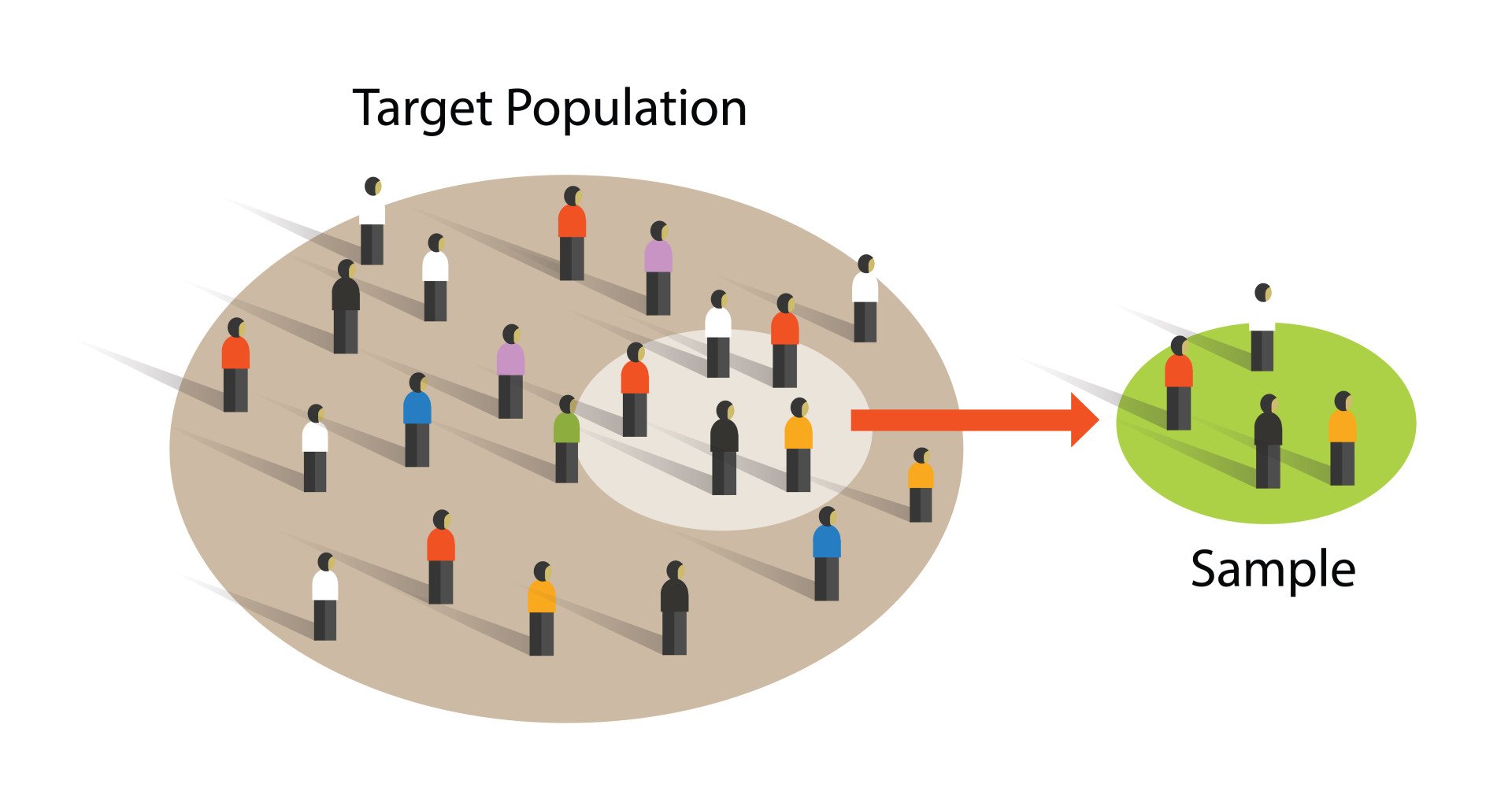
Sampling methods in psychology refer to strategies used to select a subset of individuals (a sample) from a larger population, to study and draw inferences about the entire population. Common methods include random sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and convenience sampling. Proper sampling ensures representative, generalizable, and valid research results.| Simply Psychology