Intelligence in psychology refers to the mental capacity to learn from experiences, adapt to new situations, understand and handle abstract concepts, and use knowledge to manipulate one's environment. It includes skills such as problem-solving, critical thinking, learning quickly, and understanding complex ideas.| Simply Psychology
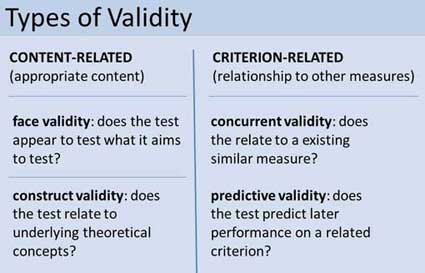
In psychology research, validity refers to the extent to which a test or measurement tool accurately measures what it's intended to measure. It ensures that the research findings are genuine and not due to extraneous factors. Validity can be categorized into different types, including construct validity (measuring the intended abstract trait), internal validity (ensuring causal conclusions), and external validity (generalizability of results to broader contexts).| Simply Psychology