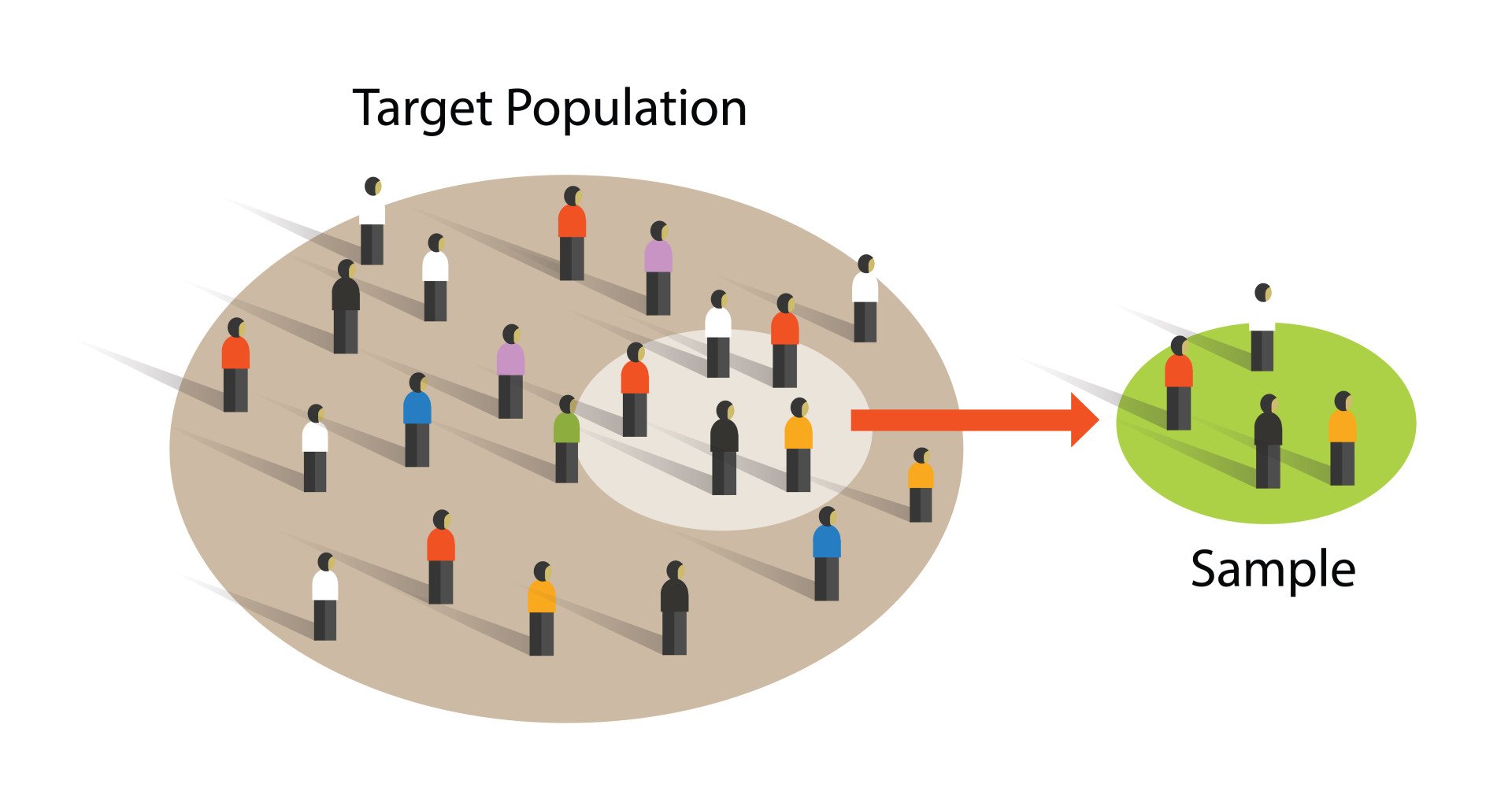
Convenience Sampling (Accidental Sampling): Definition, Method & Examples
Convenience sampling is a non-probability sampling method where data is collected from an easily accessible and available group of people. The individuals in the sample are selected not because they are most representative of the entire population, but because they are most easily accessible to the researcher.| Simply Psychology