What is balance billing? | healthinsurance.org
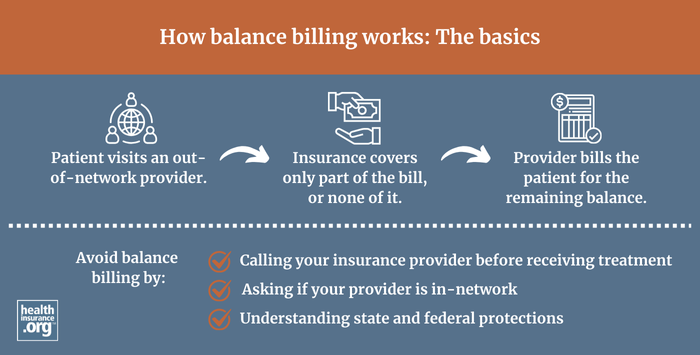
Balance billing occurs when providers bill a patient for the difference between the amount they charge and the amount that the patient's insurance approves. The negotiated rate that insurers pay providers is almost always less than the provider's "retail price." Depending on the circumstances, out-of-network providers can bill the patient for the difference, or balance; this is called balance billing. Federal rules protect patients from "surprise" balance billing as of 2022.| healthinsurance.org